Global Sourcing & Procurement
Outsourcing Service Center
In China
Export Business on Advanced Material & Precision Parts


Product & Process Engineering Process
Product & Process Engineering Process
Robert Bosch GmbH is the global leader in automotive and industry engineering, the Product & Process Engineering Process from Bosch is Representative and Persuasive.
Further more, several of our team memebers who worked for Robert Bosch GmbH`s China Plants, here we would refer to Bosch Product & Process Engineering Process:
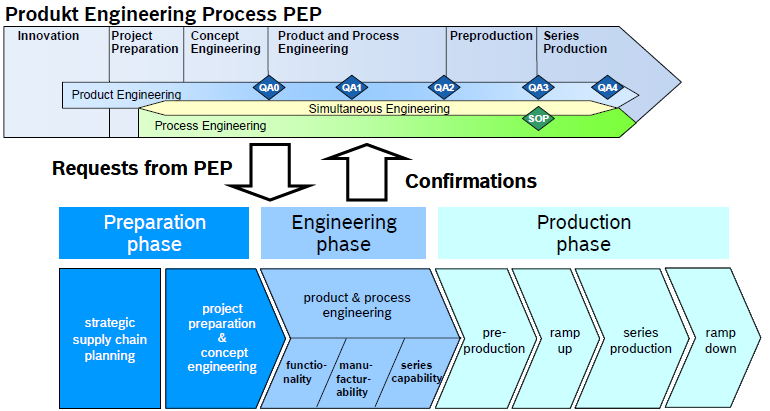
Engineering Phase
The engineering phase is split into functionality,manufacturability, and series capability phase. All series uppliers need to pass those phases before SOP. For each project there will be an individual decision to start the engineering phase with several suppliers simultaneously or to involve potential second and third sources at a later time and pass the process faster.
In any case, all purchased parts have to be released until QA2 if product changes should be avoided.
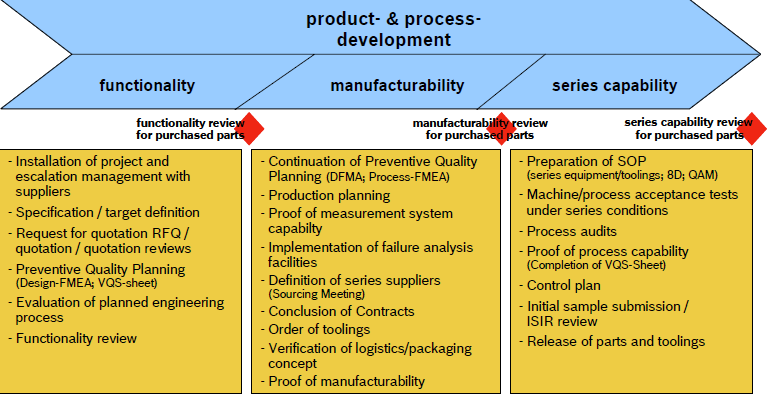
Functionality Phase
The engineering phase starts with the functionality phase. In the beginning of the functionality phase, an
adequate project- and escalation management is agreed with potential suppliers.
Component specifications, drawings, and specific product characteristics are discussed with potential
series suppliers. Project schedules, cost and quality targets as well as estimated demands and logistic
requirements have to be adjusted.
Requests for quotation are transferred together with those requirements to potential series supplier. The
supplier’s quotations are evaluated regarding Q,C,Dcriteria. The selection of potential series suppliers for
the project is based on this evaluation.
The process of preventive quality planning is started with the potential suppliers. Suppliers of important
Components are involved in a Design-FMEA(D-FMEA) or interface-FMEA respectively, in order to include their production know-how in the product design and to influence the design if necessary.
Based on the drawing and the results of the D-FMEA,the VQS-sheet is generated and discussed with the
supplier. The engineering planning of the supplier has to be evaluated.
Samples are procured in order to evaluate the functionality. The Design-FMEA should be updated with
the lessons learned from the sample phase.
The experiences of this phase are evaluated in a functionality review. Risks are escalated into PEP until QA1.
Manufacturability phase
Measures, which have been defined in the D-FMEA are implemented during the manufacturability phase.
The manufacturability is evaluated by a DFMAanalysis (design for manufacturability and assembly).
The process-FMEA (P-FMEA) is executed by the supplier and evaluated jointly. That way, the design is
being aligned with the production process of the supplier.Critical processes are added to the VQS-sheet.
Technical and commercial issues are clarified with the supplier. The production concept is developed. Therefore, a value stream design of the planned process is developed and quality control loops are planned.
Packaging and transport modes have to be defined.
The supplier has to certify manufacturability and estimated process capabilities by means of adequate
evaluations (samples, corresponding products and processes). Measurement system capabilities of series
testing machines have to be demonstrated by the supplier. Failure analysis facilities have to be installed.
Requests for quotations are updated, quotations are received and evaluated. The strategy for second and
third source (schedule for release and ramp up, etc.) and second tooling is defined. The series suppliers
selections are approved in a sourcing meeting.
To allow timely tool orders, the tool design is frozen for toolings with long lead times. For corresponding
components an individual design freeze is scheduled at the same time. Following product changes are possible by means of engineering change requests.
The estimated demands are verified and communicated to the supplier. The sub-supplier management
and the requirements for initial sample submission are defined. Contracts for series product delivery are
closed in conjunction with end-of-lifetime and ppm/PLKZ agreement, if applicable. Logistics service
providers are contracted, too.
Verification of the logistics- and packaging concept as well as the validation of the samples complete the
manufacturability phase. The results of the validation are included in the design. After that, the design is
frozen completely.
A purchasing milestone finalizes and evaluates this phase; a chance for feedback to PEP should be used.
Series capability phase
The engineering phase is concluded by the proof of series capabilities. The supplier has to ensure, that
the part can be produced on the series machines and toolings with required process capabilities. Complaints
in this phase have to be handled by means of the 8D-method and a quality assurance matrix QAM has to be installed.
The supplier has to prove process stability, machine and process capability, and the implementation of the
defined measures from the P-FMEA. Reaction criteria for statistical process control SPC have to be defined.
The VQS-sheet will be completed with the proof of the capabilities and a control plan for ramp up and series
production will be developed. The production process is released with a process audit and a process acceptance test under series conditions.
The release of the parts is based on an initial sample submission including an ISIR review. In doing so, the
supplier proves complete adherence to the specifications.
The engineering phase is concluded by the series capability review. With this review, the purchased parts are released. The review is scheduled before the QA2 of the customer product.
Samples in different levels
PPAP Documents[for automotive industry]
Design Verification and Process Verification Documents[for other industries]
VQS-Sheet: Preventive Quality Control Plan
8D Method Report
Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
is used in the automotive supply chain to establish confidence in component suppliers and their production processes, by demonstrating that all customer engineering design record and specification requirements are properly understood by the supplier and that the process has the potential to produce product consistently meeting these requirements during an actual production run at the quoted production rate.
