Global Sourcing & Procurement
Outsourcing Service Center
In China
Export Business on Advanced Material & Precision Parts


Lean Supply Chain Management
Hay Think`s Lean Management System Derive From
TPS: Toyota Production System
BPS: Bosch Production Systtem
HPS: Hay Production System:
The cornerstone of production strategy is the”Lean Production System” (HPS), designed to eliminate waste in production and all related business processes. HPS provides the basis for continuous improvements in quality, costs, and supply performance. We actively involve our suppliers in HPS activities and offer HPS training courses.
Furthermore we use special supplier development projects to jointly work on the implemenation of HPS principles. The aim is to continuously improve the productivity of our manufacturing chain.
The standardized lean processes based on HPS call for smooth, uninterrupted operations. That means our suppliers have to meet our requirements regarding flexibility, delivery frequency, and replenishment lead time – in a word, they must be “HPS compatible.”
14 Principles of Lean Toyota Production System (TPS)
Principle 1: Base your management decisions on a long term philosophy, even at the expense of short-term financial goals.
Principle 2: Create continuous process flow to bring problems to the surface.
Principle 3: Use “Pull” system to avoid overproduction.
Principle 4: Level out the workload (heijunka). (“Work like a tortoise, not the hare”).
Principle 5: Build a culture of stopping to fix problems, to get quality right at the first time.
Principle 6: Standardized tasks are the foundation for continuous improvements and employee empowerment.
Principle 7: Use Visual Control so no problems are hidden.
Principle 8: Use only reliable, thoroughly tested technology that servers your people and process.
Principle 9: Grow leaders who thoroughly understands the work, live philosophy and teach it to others.
Principle 10: Develop exceptional people and teams who follow your company’s philosophy.
Principle 11: Respect your extended network of partners and suppliers by challenging them and helping them improve.
Principle 12: Go to gemba and see for yourself to thoroughly understand the situation (Genchi Genbutsu).
Principle 13: Make decision slowly by consensus (use cross functional teams), thoroughly considering all options; implement decisions rapidly.
Principle 14: Become a learning organization through relentless reflection (hansei) and continuous improvements (Kaizen).
Supply Chain Excellence Management
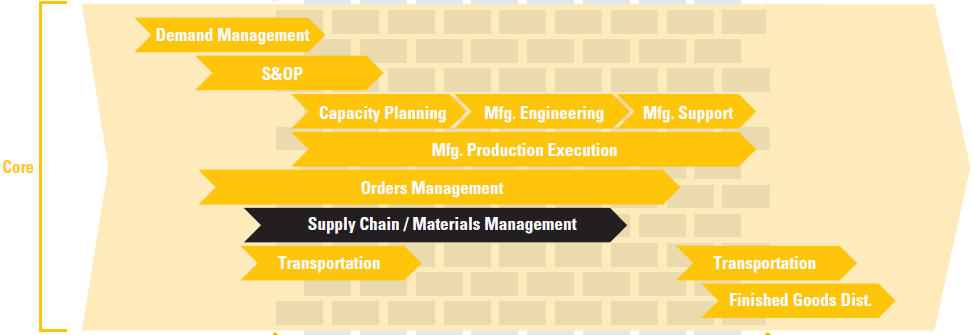
Supply Chain Strategies Management
Supply Chain Vision
Our goal is to establish Hay Think`s Supplier as the leader in global manufacturing and deliver the highest customer value. We will implement a lean, integrated Supply Chain with 6 Sigma levels of performance for:
• On-Time Delivery
• On-Time Shipment
• Percent of Spend on Pull Replenishment
• Record Accuracy
• Inventory Turns
• Point of Use Availability
The supply chain will safely deliver top-quality products at the lowest cost while increasing our velocity; thus generating a competitive advantage through superior supply chain execution.
As one of the core Hay Production System (HPS) business processes, the Supply Chain / Materials Management process is a key enabler to other core processes such as Order Management and Finished Goods Distribution.
Supply Chain Strategies
Push to Pull Replenishment Strategy
Supplier Collaboration
Total Cost of Ownership
Supply Chain Planning Management
The Medium And Long-term Planning Of The Supply Chain Includes
Supply chain organization planning and team capacity planning
Supply chain performance evaluation system planning
Analysis of supply chain cost driving factors and cost reduction plan
Available capacity planning
PFEP
Strategic Supply Chain Network Design and Planning
Layout planning and design of logistics center
Supply chain business process planning and reengineering
Logistics Information Planning and Implementation
Planning and implementation of logistics automation system
Optimization of inventory strategy
Warehousing planning
Packaging planning
…
The Short-term Supply Chain Planning Includes
Demand Management and Demand Planning
S & OP Sales and Operations Planning
Collaborative planning [forecasting and supplementation]
[PMC Production Material Control / Production Material Control [PC Production Control and MC Material Control System]]
MPS Master Production Planning
RCCP Rough-Cut Capability Planning
MRP
CRP Capacity requirements planning
PAC production operations and scheduling
FAS Final Assembly scheduling
Inventory planning
…
Supply Chain Execution Management
Operating Model
Basic Requirements for Replenishment Planning
Plan for Every Part[PFEP]
Replenishment Methods
Facility Replenishment Strategy Applying OSS
Fixed Build Sequence
Supply Chain Visibility
Process Variation
Internal Material Flow
Supplier Collaboration
Inventory Management
Packaging
Transportation
1. Information Management In Logistics
2. Control concepts and order processing
2.1 Control concepts
KANBAN
VMI including consignment
Call-off | PO | ROP Pull
2.2 Flexibility and release periods
Production and material releases
Minimum order quantities
Flexibility
Start-up and phase-out control
3. Packaging Planning
3.1 Packaging specifications
Packaging design criteria
Responsibilities and definition of packaging specification
Permitted and non-permitted materials
Delivery specifications
Requirements for electrostatic discharge (abbr.: ESD) protection
Corrosion prevention and moisture control
Packaging for hazardous goods
3.2 One-way packaging
Specification
Procurement
Specific requirements depending on transportation type
3.3 Returnable packaging
Specification depending on type of returnable packaging
Empties management
Provision and storage of customer-returnable empties
Repairs and scrapping
Cleaning
Labeling of customer-returnable packaging by the SUPPLIER
Customer standards for returnable SLC
Adapter pallets and roller carriages
4. Transport logistics
4.1 Basic information on shipping from SUPPLIER to customer
Transportation companies, couriers, and package shipments
Packages and HUs
4.2 Shipping and transportation documents
Shipping documents
Transport documents
4.3 Labeling of products
4.4 Transport notification
Transports not processed through Customer TMC
Transports processed through Customer TMC
Special arrangements for transportation of critical goods
4.5 Label for sample parts
4.6 ASN
4.7 Shipping process
4.8 Security in goods transportation
5. Special transports and variation management
5.1 Special transports
5.2 Variation management
5.3 Risk and crisis management in logistics
Background
Definition, tasks, and objectives
6. Logistics quality
Logistics complaints
SUPPLIER Result Assessment (abbr.: LEB) – Logistics
Controlling of logistics performance by SUPPLIER
Special transports and variation management
Special transports
Variation management
Risk and crisis management in logistics
Background
Definition, tasks, and objectives
Logistics quality
Definition
Logistics complaints
SUPPLIER Result Assessment (abbr.: LEB) – Logistics
Controlling of logistics performance by SUPPLIER
Supply Chain And Material Management Manual
Supply Chain Excellence Management To Deliver Added Value
